One common graph storage format is called an adjacency list.
In this format, every node has a list of connected neighbors: an adjacency list. We could store these lists in a dictionary where the keys represent the node and the values are the adjacency lists.
For instance, here's one graph:

And, here's how we'd represent it using a dictionary:
Since node 3 has edges to nodes 1 and 2, graph[3] has the adjacency list [1, 2].
Interview coming up?
Get the free 7-day email crash course. You'll learn how to think algorithmically, so you can break down tricky coding interview questions.
No prior computer science training necessary—we'll get you up to speed quickly, skipping all the overly academic stuff.
No spam. One-click unsubscribe whenever.
You're in! Head over to your email inbox right now to read day one!
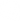 Interview Cake
Interview Cake
